Introduction
The TPA3116D2DADR is are digital amplifier that is stereo-efficient. They can be used as a power stage to drive speakers with up to 100W / two in mono. Three devices share the same footprint, which allows one PCB to function across multiple power settings. Its advanced oscillator/PLL circuit utilizes an option to switch frequencies in multiple ways to reduce AM interference. This is done by using the choice of either master or slave options, which allows you to sync multiple devices. The TPA3116D2DADR amplifier is widely used in mini-micro components, speaker bars, docks, and as well as consumer audio applications.
- Complete Guide to Electronics Engineering
- Traction Control Sensor TCS: Working and Common Fault Signs
Features
- Supports Multiple Output Configurations
- Wide Voltage Range: 4.5 V to 26 V
- Efficient Class-D Operation
- Multiple Switching Frequencies
- Feedback Power-Stage Architecture With High PSRR Reduces PSU Requirements
- Programmable Power Limit
- Differential and Single-Ended Inputs
- Stereo and Mono Mode With Single-Filter Mono Configuration
- Single Power Supply Reduces Component Count
- Thermally Enhanced Packages
- –40°C to 85°C Ambient Temperature Range
CAD Model
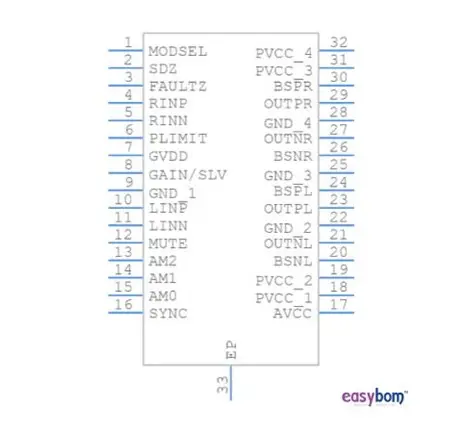

Specifications
Supply Chain
- Factory Lead Time – 6 Weeks
- Lifecycle Status – ACTIVE
Physical
- Contact Plating – Gold
- Mount – Surface Mount
- Number of Pins – 32
Technical
- Operating Temperature – -40°C~85°C TA
- JESD-609 Code – e4
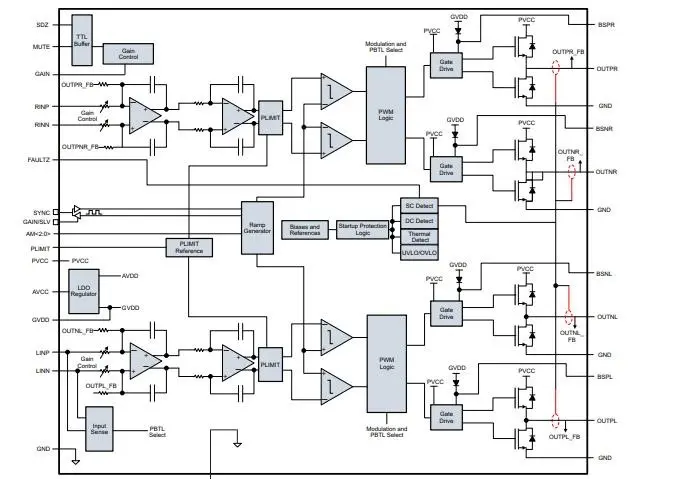
Circuits of TPA3116D2DADR
Alternative Models
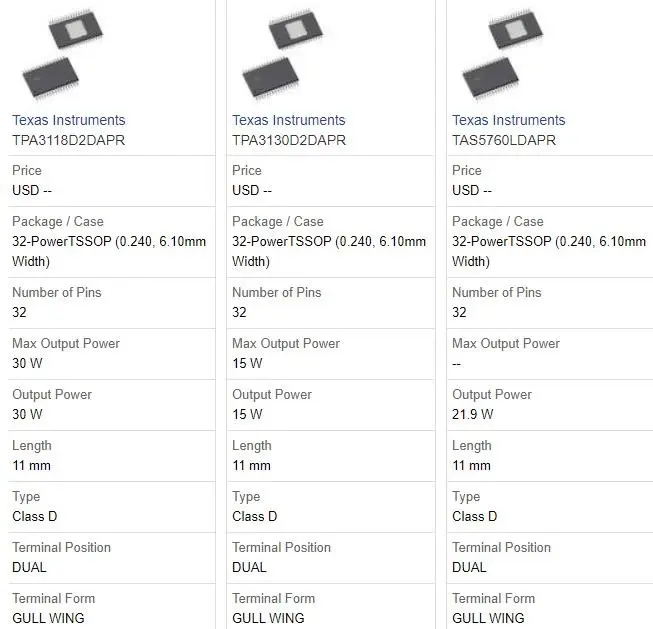
TPA3118D2DAPR, TPA3130D2DAPR, TAS5760LDAPR
Where to Use TPA3116D2DADR?
The TPA3116D2DADR amplifier is a device that is used to increase the level of a signal so that it can be transmitted more efficiently. It has different uses in a variety of markets, such as in the fields of telecommunication and music. The major components in an amplifier are usually a power amplifier, which handles the input power from the source, and amplifiers themselves, which amplify the input signal before passing it on to other devices.
- Crane Electrical Systems: Safe, Intelligent, and Efficient Operation
- Electrical Installation Guide: Wiring, Protection & Safety Standards
The TPA3116D2DADR amplifier can be made in many different ways, but the most common is what is known as the transistor amplifier circuit. A transistor amplifier circuit uses one or more transistors to amplify a signal. The input signal passes through the base of the transistor, and the output is collected at its emitter or collector terminal.

How to Use TPA3116D2DADR Amplifier?
The TPA3116D2DADR amplifier works by taking the incoming energy from the power supply and delivering this energy to its output in very precise quantities during each cycle of operation. An ideal op-amp with infinite gain will take one input voltage at its inverting terminal, amplify it according to some factor determined by external circuitry, and then send that amplified signal out on its non-inverting terminal. If the input is one volt, for example, the output will be two volts. The amplifier may then take several cycles to process this voltage before producing another output.
Parts with Similar Specs
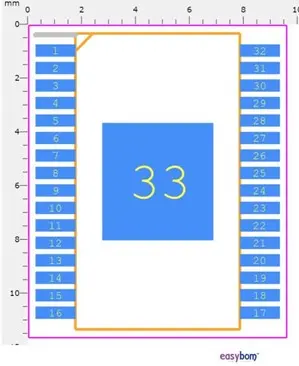
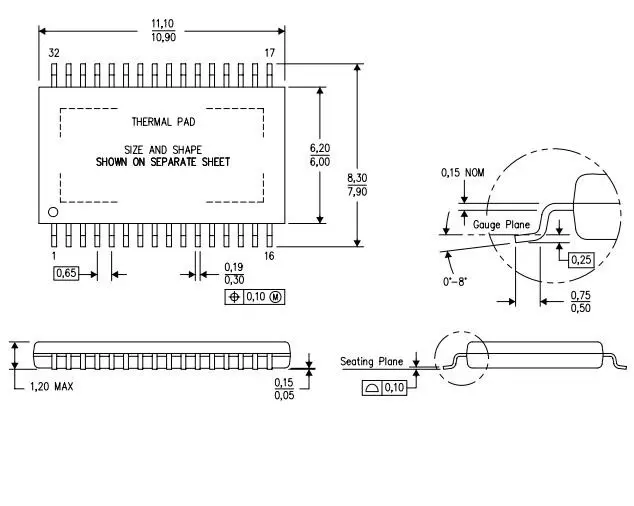
Package Dimensions
About the Manufacturer
Texas Instruments (TI) emerged as a globally recognized semiconductor manufacturer and expanded into 35 countries. It has seen rapid growth. In 1958, they first introduced the working integrated circuit. They aspire to solve challenges as well as change the world through their technologies.
Datasheet
https://www.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/tpa3116d2.pdf
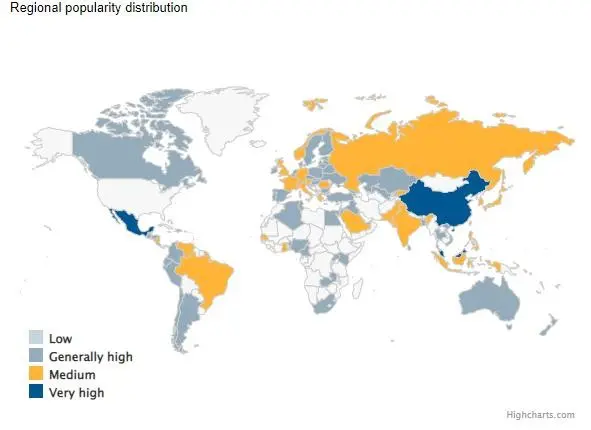
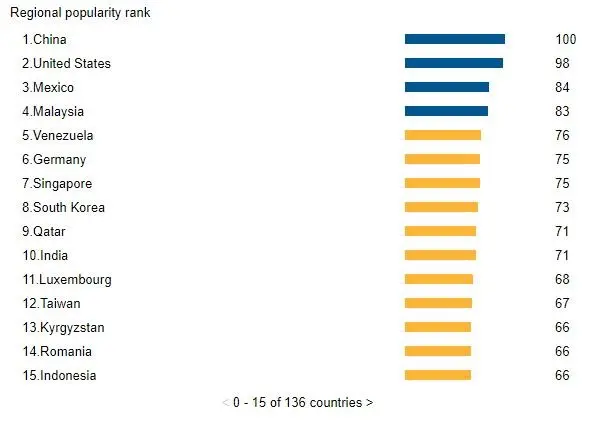
Popularity by Region
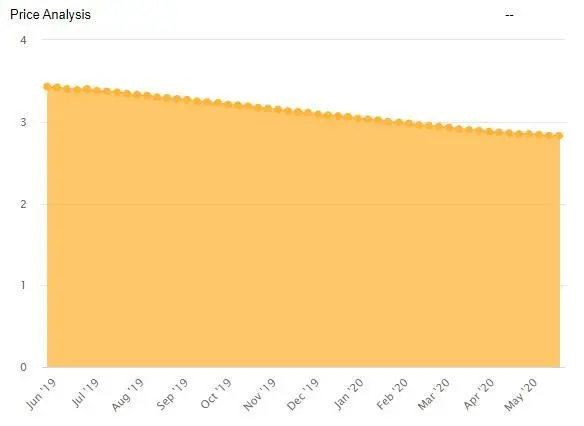
Trend Analysis
- Complete Guide to Circuit Analysis in Electrical Engineering
- Managing Your Digital Objectives – Short and Long-Term
Conclusion
The TPA3116D2DADR amplifier is a device that increases the signal power, which is generated by sending current. Amplifiers are usually connected to wires or speaker terminals using output connectors. The most common types are vacuum tubes, solid-state, and hybrid amplifiers. Easybom believes that the TPA3116D2DADR amplifier prevents malfunctions through thermal protection and short-circuit protection, over-voltage or under-voltage protection, and DC protection. The fault will be reported to the processor to prevent damage to the device under overload conditions.