The encoder in CNC machine technology plays a vital role in ensuring accuracy, speed, and reliability. Without encoders, CNC machines would not be able to achieve the precision required for modern manufacturing. From shaping aerospace components to producing detailed woodworking designs, encoders are the hidden heroes. Choosing the right encoder is essential for smooth operation, cost efficiency, and long-term machine performance.
What is an Encoder in a CNC Machine
An encoder in CNC machines is a sensor device that converts motion into electrical signals. These signals provide information about position, direction, and speed, which are then used by the machine’s control system. Encoders make it possible for the cutting tool or spindle to move with accuracy down to fractions of a millimeter.
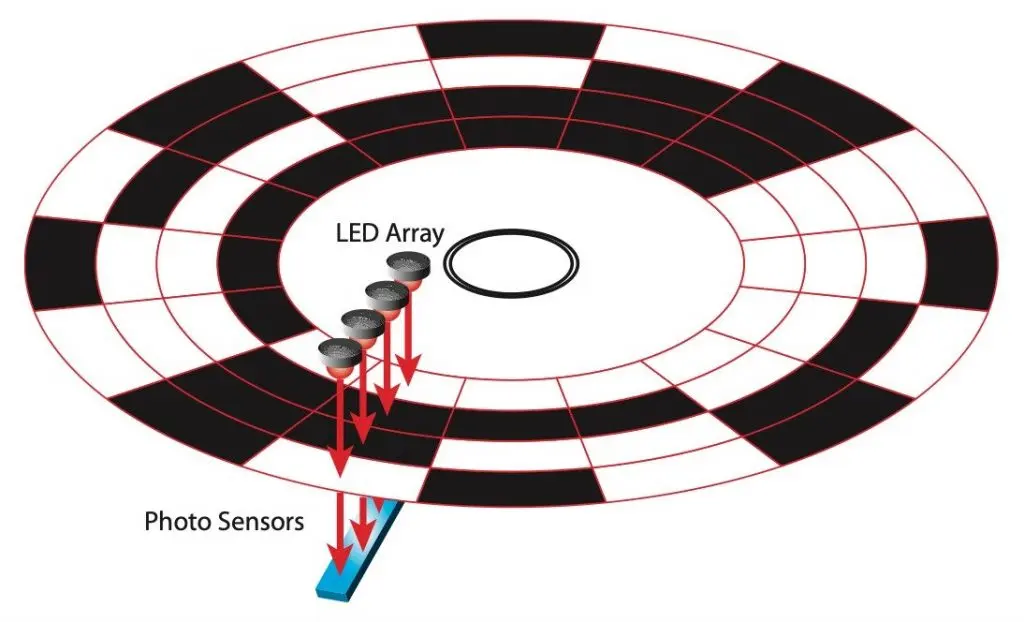
In CNC machines, there are two main types of encoders: rotary and linear. Rotary encoders measure angular movement, while linear encoders measure straight-line displacement. Both types provide the critical feedback needed to keep CNC tools operating within tight tolerances.
Why Encoders Matter in CNC Performance
Encoders are at the heart of CNC precision. Their role is not limited to monitoring movement; they actively contribute to the performance and safety of the entire machine.
- Accuracy: By tracking exact positions, encoders help achieve consistent and flawless cuts.
- Speed Control: CNC spindles and motors rely on encoders for stable speed and load balancing.
- Reliability: High-quality encoders reduce errors and downtime, saving costs in industrial operations.
Without an encoder, CNC machines would lack the feedback necessary for automated, precise control.
Types of Encoders Used in CNC Machines
Different CNC applications require different encoders. The most common ones include:
- Crane Electrical Systems: Safe, Intelligent, and Efficient Operation
- Electrical Installation Guide: Wiring, Protection & Safety Standards
Rotary Encoders
These measure rotation and are attached to motors and spindles. They are essential for tasks that require tracking angular movement.
Linear Encoders
These provide feedback on straight-line motion. They are often used in CNC milling machines where precise linear positioning is critical.
Absolute vs Incremental Encoders
- Absolute encoders provide a unique digital code for every position, ensuring no loss of data if the machine is powered down.
- Incremental encoders provide relative position information and are often more cost-effective. For a deeper technical explanation, you can read more about incremental encoders from a high-authority source.
Selecting between absolute and incremental depends on the CNC application’s precision and memory requirements.
Encoder in Automation: Beyond CNC
The role of encoders goes beyond CNC machines. In the wider field of automation, encoders are essential in:
- Robotics, where encoders ensure arms move to exact positions
- Conveyor belts, where they control speed and placement
- Packaging machinery, where timing and synchronization depend on precise feedback
Using an encoder in automation means efficiency, reduced waste, and higher safety standards. This crossover highlights how choosing the right encoder benefits both CNC and general industrial automation.
How to Choose the Right Encoder for CNC Applications
When selecting an encoder for a CNC machine, consider the following factors:
- Resolution: Determines how detailed the movement feedback is. Higher resolution is better for fine cutting.
- Environment: Dust, temperature, and vibration can affect encoder performance. Industrial-grade encoders with seals are better in harsh conditions.
- Durability: Choose encoders with proven life cycles for continuous operations.
- Machine Type: Different CNC machines, like lathes or milling systems, may require specific encoder designs.
- Budget: While high-end encoders offer more features, many cost-effective models under standard industrial brands can deliver excellent results.
The right encoder balances performance and cost, making it a smart long-term investment.
- Complete Guide to Electronics Engineering
- Traction Control Sensor TCS: Working and Common Fault Signs
Challenges and Maintenance Tips
Like all machine components, encoders can face wear and tear. Some common challenges include:
- Dust and Debris: CNC workshops often produce particles that can affect sensor accuracy.
- Vibration: Excessive vibration may loosen encoder fittings.
- Electrical Noise: Interference from motors can distort signals.
To extend the life of an encoder:
- Regularly clean the housing
- Check alignment and mounting screws
- Use shielding for cables to prevent electrical interference
These small steps ensure reliable encoder performance over the long term.
Final Thoughts
The encoder in a CNC machine is not just a supporting component but a central feature that defines accuracy, efficiency, and safety. Whether you are working on precision milling, high-speed cutting, or industrial automation, the right encoder ensures consistent performance. From absolute models to incremental designs, encoders are the backbone of both CNC systems and wider automation solutions. Investing in the correct type of encoder is one of the most important decisions in maintaining high-quality production standards.
FAQs
What is the role of an encoder in a CNC machine?
It provides feedback on speed and position, ensuring precise tool movement and accurate machining.
Which type of encoder is best for CNC?
It depends on the application. Absolute encoders are best for uninterrupted accuracy, while incremental ones are cost-effective and reliable for most tasks.
How is the encoder in automation different from CNC use?
In CNC, encoders mainly focus on precision in cutting and positioning. In automation, they are used for broader tasks like robotics, conveyors, and packaging.
