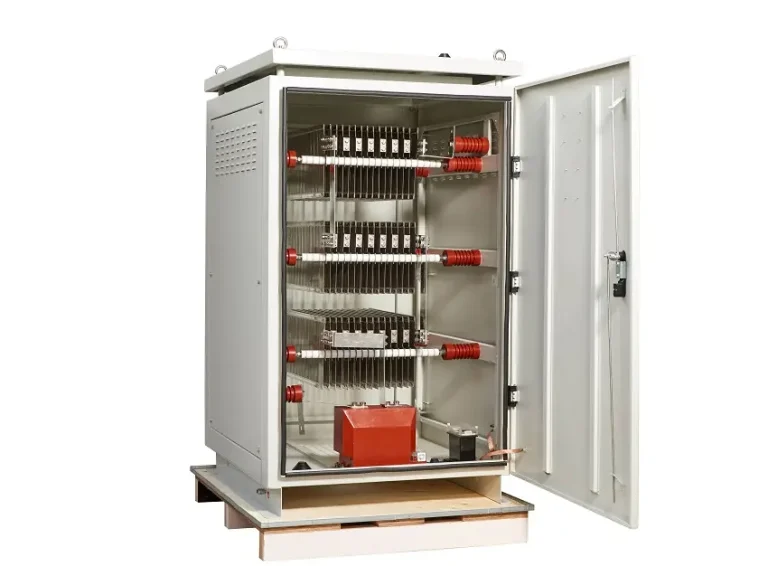
In the world of electrical systems, safety and stability are paramount. One critical component that plays a vital role in achieving these goals is the neutral grounding resistor (NGR). Often overlooked but essential, NGRs are used to limit fault currents in electrical systems, protect equipment, and ensure the safety of personnel. In this post, we’ll dive into the details of neutral grounding resistors, answer questions like what a neutral ground resistor is and how a neutral ground resistor works, and explore their importance in modern electrical systems.
- Crane Electrical Systems: Safe, Intelligent, and Efficient Operation
- Electrical Installation Guide: Wiring, Protection & Safety Standards
What is a Neutral Ground Resistor?
A neutral grounding resistor is a device used in electrical systems to limit the current that flows through the neutral point of a transformer or generator during a ground fault. By introducing resistance into the grounding path, NGRs reduce the fault current to a safe level, preventing damage to equipment and minimizing the risk of electrical fires or shocks. They are commonly used in industrial, commercial, and utility power systems where safety and reliability are critical.
Why Are Neutral Grounding Resistors Important?
- Fault Current Limitation: NGRs limit the magnitude of ground fault currents, reducing the risk of damage to transformers, generators, and other equipment.
- Enhanced Safety: By controlling fault currents, NGRs protect personnel from electric shocks and minimize the risk of arc flashes.
- System Stability: NGRs help maintain system stability during ground faults, preventing sudden voltage fluctuations and ensuring uninterrupted operation.
- Equipment Protection: Limiting fault currents reduces thermal and mechanical stress on electrical components, extending their lifespan.
- Compliance with Standards: Many electrical codes and standards require the use of NGRs in specific applications to ensure safe and reliable operation.
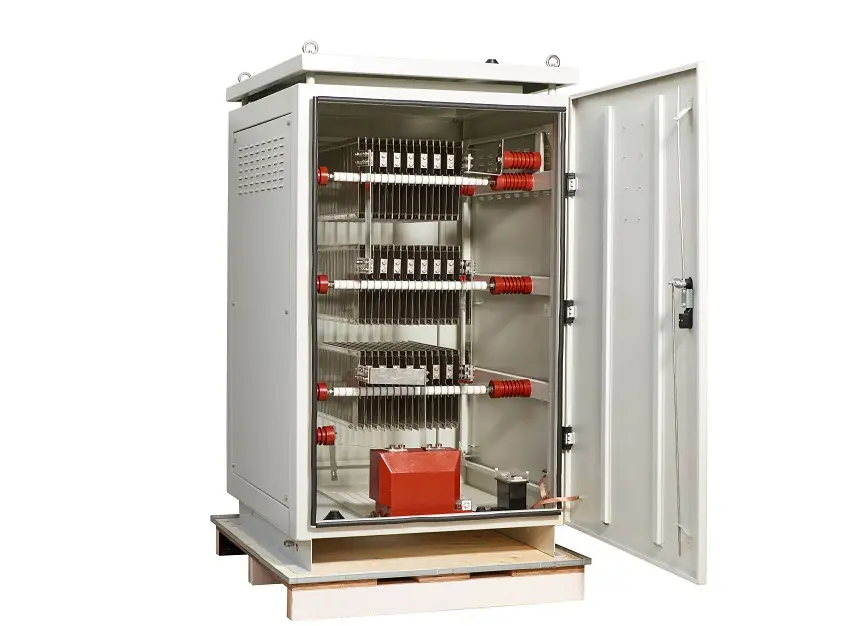

How Does a Neutral Ground Resistor Work?
To understand how a neutral ground resistor works, let’s break it down step by step:
- System Configuration: In a grounded electrical system, the neutral point of a transformer or generator is connected to the ground through a neutral grounding resistor.
- Normal Operation: Under normal conditions, the current flows through the phase conductors, and the neutral point remains at or near ground potential.
- Ground Fault Occurrence: When a ground fault occurs (e.g., a phase conductor comes into contact with the ground), current flows through the fault path and the neutral grounding resistor.
- Current Limitation: The resistor limits the fault current to a predetermined safe level, typically between 5% and 10% of the system’s full-load current. This prevents the fault current from reaching dangerous levels.
- Fault Detection: The limited fault current is still sufficient to trigger protective devices like relays or circuit breakers, which isolate the fault and protect the system.
- System Restoration: Once the fault is cleared, the system can be restored to normal operation with minimal disruption.
- Complete Guide to Electronics Engineering
- Traction Control Sensor TCS: Working and Common Fault Signs
Types of Neutral Grounding Resistors
Neutral grounding resistors come in various types, each suited for specific applications:
- Low-Resistance NGRs: These resistors limit fault currents to a higher value (typically 100-400 amps) and are used in systems where selective fault detection is required.
- High-Resistance NGRs: These resistors limit fault currents to a very low value (typically 5-10 amps) and are used in systems where continuous operation during a fault is critical.
- Liquid NGRs: These resistors use a conductive liquid as the resistive element and are often used in high-voltage applications.
- Solid NGRs: These resistors use solid resistive elements and are commonly used in low- and medium-voltage systems.
Applications of Neutral Grounding Resistors
Neutral grounding resistors are used in a wide range of applications, including:
- Power Generation: NGRs are used in generators and transformers to protect against ground faults and ensure stable operation.
- Industrial Facilities: Manufacturing plants, refineries, and other industrial facilities use NGRs to safeguard equipment and personnel.
- Commercial Buildings: Hospitals, data centers, and office buildings rely on NGRs to maintain power quality and prevent downtime.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Solar and wind power systems use NGRs to protect inverters and other critical components.
1. What is a neutral ground resistor?
A neutral ground resistor is a device used to limit the current that flows through the neutral point of a transformer or generator during a ground fault, ensuring safety and system stability.
2. How does a neutral ground resistor work?
A neutral ground resistor works by introducing resistance into the grounding path, limiting the fault current to a safe level, and allowing protective devices to isolate the fault.
3. Why is a neutral grounding resistor necessary?
NGRs are necessary to protect equipment, ensure personnel safety, maintain system stability, and comply with electrical codes and standards.
4. What are the types of neutral grounding resistors?
The main types of NGRs are low-resistance, high-resistance, liquid, and solid resistors, each suited for specific applications and system requirements.
Conclusion
The neutral grounding resistor is a small but mighty component that plays a crucial role in ensuring the safety, stability, and reliability of electrical systems. By limiting fault currents and protecting equipment, NGRs help prevent costly downtime, equipment damage, and safety hazards. Whether you’re working with power generation systems, industrial facilities, or renewable energy installations, understanding what a neutral ground resistor is and how a neutral ground resistor works is essential for designing and maintaining safe and efficient electrical systems.
